- छद्म- अनियमित नम्बर जेनेरेटर (PRNG) C++ मा
- C++
- rand () र srand ()
- C++ Random Float
- C++ Random Number Between 0 And 1
- C++ Random Number Between 1 And 10
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Conclusion
यस ट्युटोरियलले C++ मा अनियमित नम्बरहरू उत्पन्न गर्न विस्तृत रूपमा कार्यहरू rand() र srand() को प्रयोग वर्णन गर्दछ:
धेरै पटक हामीले उत्पादन गर्न हाम्रो अनुप्रयोगमा अनियमित संख्याहरू प्रयोग गर्न आवश्यक छ। सिमुलेशन वा खेल र अन्य एप्लिकेसनहरू जसलाई अनियमित घटनाहरू आवश्यक पर्दछ।
उदाहरणका लागि, पासाको खेलमा, अनियमित घटनाहरू बिना, हामीले प्रत्येक पटक फ्याँक्दा उही पक्ष पप अप हुनेछ। पासाले अवांछनीय परिणामहरू दिन्छ।
यसैले यो आवश्यक हुन्छ कि हामीसँग अनियमित संख्या जनरेटर छ। भौतिक वातावरणमा, हामीले अनियमित घटनाहरू उत्पन्न गर्न सक्छौं तर कम्प्युटरहरूमा आउँदा यो सम्भव छैन।
यसको कारणले गर्दा कम्प्युटरमा भएका सबै कुराहरू बाइनरी हुन्छन् अर्थात् ० वा १ (सत्य वा गलत) र बीचमा केही हुँदैन। त्यसैले कम्प्यूटरहरूले प्राय: अनुमानित घटनाहरू उत्पन्न गर्छन् र अनियमित घटनाहरू उत्पन्न गर्न सक्षम हुँदैनन्।

बरु, कम्प्युटरहरूले अनियमितता अनुकरण गर्दछ जुन स्यूडो-रेन्डम नम्बर जनरेटर (PRNG) प्रयोग गरी गरिन्छ। । C++ सँग अनियमित संख्या जनरेटर छ र धेरै अनुप्रयोगहरूमा प्रयोग गर्न सकिन्छ।
यस ट्यूटोरियलमा, हामी C++ मा अनियमित संख्याहरू उत्पन्न गर्ने कार्यहरू/उपक्रमहरू विस्तारमा छलफल गर्नेछौं।
छद्म- अनियमित नम्बर जेनेरेटर (PRNG) C++ मा
सामान्यतया, एक छद्म-यादृच्छिक संख्या जनरेटर (PRNG) लाई एउटा कार्यक्रमको रूपमा परिभाषित गर्न सकिन्छ जसले बीज वा सुरूवात संख्या लिन्छ र यसलाई फरक फरक संख्यामा रूपान्तरण गर्दछ। बीउबाटगणितीय अपरेसनहरू प्रयोग गर्दै।
यो प्रक्रिया प्रत्येक पटक अन्तिम उत्पन्न संख्या लिएर बारम्बार गरिन्छ। प्रत्येक पटक उत्पन्न गरिएको संख्या अघिल्लो संख्याहरूसँग सम्बन्धित छैन। यसरी यो कार्यक्रमले अनियमित देखिने संख्याहरूको शृङ्खला उत्पन्न गर्न सक्षम छ।
C++ भाषा एक इन-बिल्ट स्यूडो-रेन्डम नम्बर जनरेटरको साथ आउँछ र दुई प्रकार्य rand () र srand () प्रदान गर्दछ जुन प्रयोग गर्न सकिन्छ। अनियमित संख्याहरू उत्पन्न गर्नुहोस्।
यी दुई प्रकार्यहरू विस्तृत रूपमा छलफल गरौं।
C++
srand ()
0 फंक्शन प्रोटोटाइप:void srand (अहस्ताक्षरित int seed);पैरामिटरहरू: बीज - छद्म-यादृच्छिक संख्या जनरेटर एल्गोरिथ्मद्वारा बीजको रूपमा प्रयोग गरिने एक पूर्णांक मान। .
रिटर्न मान: कुनै पनि छैन
विवरण: srand प्रकार्य 'random' नामक प्यारामिटरको साथ छद्म-यादृच्छिक संख्याहरूको अनुक्रम सुरु गर्न प्रयोग गरिन्छ। बीज'। यसले र्यान्ड प्रकार्यको आउटपुटलाई अनियमित देखिन्छ। अन्यथा, र्यान्ड () प्रकार्यको आउटपुट हामीले यसलाई प्रत्येक पटक कल गर्दा उस्तै हुनेछ।
यसैले, यदि हामीले srand () प्रकार्यसँग अनियमित नम्बर जनरेटरलाई सीड गर्छौं भने, यसले जेनेरेटरलाई बिन्दुबाट सुरु गर्नेछ। जुन srand मा पास गरिएको तर्क मानमा निर्भर हुन्छ। यदि हामीले प्रणाली समयको साथ अनियमित नम्बर जनरेटर सेट गर्यौं भने उदाहरणका लागि, rand () प्रकार्यमा पहिलो कल हुनु अघि, त्यसपछि हामीले प्रत्येक पटक चलाउँदा यसले अनियमित नम्बरहरू उत्पन्न गर्नेछ।कार्यक्रम।
ध्यान दिनुहोस् कि हामीले सामान्यतया srand () प्रकार्यलाई कल टु र्यान्ड () प्रकार्य अघि एक पटक मात्र कल गर्न आवश्यक छ र हरेक पटक हामीले अनियमित नम्बरहरू उत्पन्न गर्दा होइन।
rand ( )
प्रकार्य प्रोटोटाइप: int rand (void);
पैरामिटरहरू: कुनै पनि छैन
फिर्ता मान: ० र RAND_MAX बीचको एक पूर्णांक मान।
विवरण: rand () प्रकार्यले अनुक्रममा अर्को अनियमित संख्या उत्पन्न गर्छ। उत्पन्न गरिएको संख्या ० र RAND_MAX बीचको छद्म-यादृच्छिक पूर्णांक हो। RAND_MAX हेडरमा सामान्यतया 32767 मानमा सेट गरिएको स्थिर हो।
#include #include #include int main() { std::srand(static_cast(std::time(nullptr))); for (int count=1; count = 100; ++count) { std::cout std::rand() "\t"; // display 5 random numbers per row if (count % 5 == 0) std::cout "\n"; } return 0; } आउटपुट:
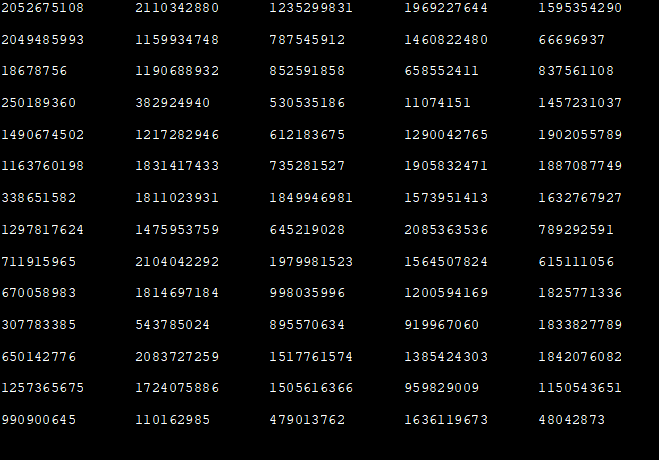
माथिको कार्यक्रममा, हामीले srand प्रकार्यको लागि बीजको रूपमा प्रणाली घडी दिएर पहिलो 100 अनियमित संख्याहरू उत्पन्न गर्यो। यस कार्यक्रममा, हामीले दुबै srand र rand प्रकार्यहरू प्रयोग गरेका छौं। ध्यान दिनुहोस् कि सीडको रूपमा प्रणाली घडी भएकाले, हामीले कार्यक्रम कार्यान्वयन गर्दा हरेक पटक उत्पन्न हुने आउटपुट फरक हुनेछ।
rand () र srand ()
| srand() | |
|---|---|
| यादृच्छिक संख्याहरू उत्पन्न गर्न प्रयोग गरिन्छ। | rand () प्रकार्यद्वारा प्रयोग गरिएको PRNG को बीजहरू। |
| हामीले अनियमित नम्बरहरू जेनेरेट गर्न चाहेको जति पटक कल गरियो। | यान्डम नम्बर जनरेटर हेर्नको लागि एक पटक मात्र कल गरियो। |
| कुनै पनि आर्गुमेन्ट लिदैन। | यान्डम नम्बर जेनेरेटर सीड गर्न प्रयोग गरिने प्यारामिटर लिन्छ। |
| को क्रम फर्काउँछप्रत्येक पटक कल गर्दा अनियमित संख्याहरू। | मान फर्काउँदैन। |
C++ Random Float
rand () प्रकार्य जुन हामीले माथि देख्यौं पूर्वनिर्धारित रूपमा पूर्णांक मान फर्काउँछ जसले केहि केसहरूमा ओभरफ्लो हुन सक्छ। यसरी, हामी फ्लोट वा डबल मान प्रयोग गर्न सक्छौं। हामी rand () प्रकार्यको रिटर्न मान 'फ्लोट' मा कास्ट गरेर फ्लोट अनियमित संख्याहरू उत्पन्न गर्न सक्छौं।
यसैले निम्नले फ्लोट 0.0 र 1.0 (दुबै समावेशी) बीचको अनियमित संख्या उत्पन्न गर्नेछ।
coutSimilarly, the below line will generate a random number between 1.2 and 3.4
cout1.2 + static_cast (rand()) / ( static_cast (RAND_MAX/(3.4-1.2)));In our subsequent example below we make use of random float to generate the output.
C++ Random Number Between 0 And 1
We can use srand () and rand () function to generate random numbers between 0 and 1. Note that we have to cast the output of rand () function to the decimal value either float or double.
The default return value of rand () function i.e. integer is inadequate to display random numbers between 0 and 1 which are fractions.
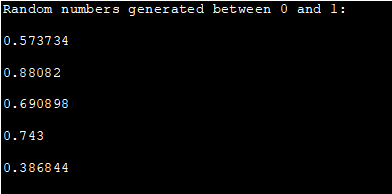
C++ program given below displays the first five random numbers between 0 and 1.
#include #include using namespace std; int main() { cout"Random numbers generated between 0 and 1:"="" ="" cout="" endl;="" for="" i="" i++)="" null="" pre="" rand()="" rand_max="" return="" srand(="" {="" }="" }=""> Output:
We see that the output of the program is the random number between 0 and 1 which are fractions.
If we don’t cast the return value of rand () function to float or double, then we will get 0 as the random number.
C++ Random Number Between 1 And 10
The next example is to generate random numbers between 1 and 10. Following is the C++ program that generates random numbers.
We call the srand function with the system clock and then call the rand function with module 10 operators.
#include #include #include using namespace std; int main() { srand(time(0)); // Initialize random number generator. cout"Random numbers generated between 1 and 10:"="" cout="" for(int="" i="0;i10;i++)" pre="" return="" }=""> Output:
In the above program, we generate the first 10 random numbers between 1 and 10. Note that every time the program is run, it will generate different sets of numbers because of the srand function being called.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q #1) What is the header file for Random function in C++?
Answer: The functions to generate random numbers, rand and srand are defined in cstdlib> header of C++.
Q #2) What is Rand_max in C++?
Answer: RAND_MAX is a constant in header generally set to value 32767. The pseudo-random number generator (PRNG) generates random numbers between 0 to RAND_MAX.
Q #3) How does the random function work?
Answer: C++ supports two random functions i.e. srand () and rand ( ). The function srand () seeds the random number generator used by rand () function which generates the random number sequence depending on the initial seed provided.
Q #4) How do you srand with time?
Answer: The srand function seeds the pseudo-random number generator (PRNG) used by the rand () function. It is a standard practice to use the result of a call to time (0) as seed. This time function returns the value, a number of seconds since 00:00 hours, Jan 1, 1970, UTC (current UNIX timestamp).
Thus the value of seed changes every second. Hence every time when srand is called with time function, a new set of the random numbers is generated.
Conclusion
We have discussed Random Number Generation in detail in this tutorial. Programming languages or in general computers do not generate random numbers as they are designed to give predictive output. Hence, we need to simulate randomness.
In order to simulate randomness, we make use of pseudo-random number generator (PRNG) which is in-built in C++. Thus using the two functions, rand () and srand () we can generate random numbers in C++.
The function srand () is used to provide seed for generating random numbers while rand () function generates the next random number in the sequence.